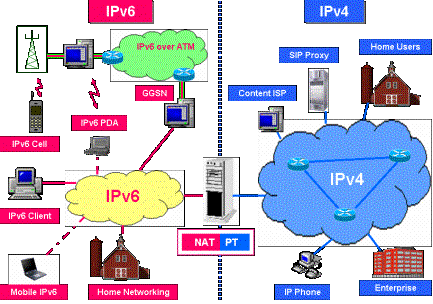
NAT-PT
By
Vikas M. Valsang
What is NAT-PT?
NAT-PT provides IPv6
/ IPv4 translation mechanism based on the standard IETF RFC 2766
NAT-PT allows native
IPv6 only hosts and applications to communicate with native IPv4 only hosts and
applications, and vice versa.
A NAT-PT device
resides at the boundary between an IPv6 and IPv4 network.
Each NAT-PT device
retains a pool of globally routable IPv4 addresses that are used to assign to
IPv6 nodes on a dynamic basis as sessions are initiated across the IPv6/IPv4
boundary.
In addition to address translation, header translation is also performed complying with IETF RFC2765 SIIT mechanism.
NAT-PT can be
extended as NAPT-PT. NAPT-PT translates based on the port address to enable the
re-use of one IPv4 pool address and map this to many IPv6 hosts.
The NAT-PT
translation device should additionally contain Application Level Gateways
(ALG).
ALG's are necessary
where IP addresses are embedded within the payload of an IP packet and require
looking inside the payload and translating those IP addresses.
Areas of Impact
1. Routing
–IPv6 unicast routing
–IPv6 multicast routing
–IPv6 anycast routing
–BGP4
–OSPFv3
2. Data Link Layer
–IP over ATM
–IP over SONET
–IP over Ethernet
–Frame Relay
3. Transition Mechanisms
–Tunneling
· 6over4
· 6to4
–Dual Stack
–Translation
· NAT
· NAT-PT
–Tunnel Broker
4. Services
–DNS using AAAA
records
–HTTP
–Telnet / FTP
–traceroute / Ping
–Neighbor
Discovery
5. Others
–Security /
Authentication
–Quality of
Service
–Mobile
NAT-PT Deployment
NAT-PT is simple to
deploy as configuration are required at the border of IPv6 / IPv4 and since
this is deployed at the network boundaries, the administration and maintenance
are relatively small.
No client
configuration is required and all the NAT-PT translation is totally transparent
to the end users.
Market Drivers for
IPv6
–Mobile Users (3rd Generation – UMTS)
–Home Networking
–Geographical Locations like Asia / Africa /
South America
–Ability to inter-network with IPv4 (IPv6
and IPv4 must co-exist)
NAT-PT Scenario